A report released earlier this week on third quarter production in Ohio’s Utica Shale has stepped-up scrutiny of just how prolific the play will be. The latest data has many drawing comparisons between the early days of Pennsylvania’s Marcellus Shale, with rising production reinforcing the Utica’s place as a gas play.
Topic / Utica Shale
SubscribeUtica Shale
Articles from Utica Shale
Air Pollution Study in Ohio Latest to Gauge Emissions in Appalachia
The University of Cincinnati and Oregon State University are partnering on a new air quality study to better understand the environmental impacts of unconventional oil and gas operations in Carroll County, Ohio, which has seen the most drilling activity in the state.
Youngstown Fracking Opponents Continue Push to Ban Drilling
Continuing with their pledge to ban fracking in Youngstown, a grassroots committee is seeking signatures for a third ballot initiative in May that would once again ask voters to amend the city’s charter, while affiliated anti-hydraulic fracturing (fracking) activists will try for the same in nearby Niles, OH.
ODNR Reports Uptick in Utica Oil, Wet Gas Production
The Ohio Department of Natural Resources (ODNR) reported a drastic improvement in horizontal well production data on Tuesday, showing a major bump in third quarter wet gas and oil production in the Utica Shale after largely disappointing figures on 2012 production it released under old annual reporting requirements in May.
ODNR Updates Pipeline Standards; Wastewater Regs Nearly Complete
The Ohio Department of Natural Resources (ODNR) has updated its pipeline standard and construction specifications, and its work to finalize draft regulations on rules for wastewater recycling is nearly complete.Shale gas development continues to accelerate in the state and as a result midstream companies plan to spend about $40 billion on infrastructure projects over the next three to five years in Ohio, West Virginia and Pennsylvania, according to one analysis by Marcellus Drilling News (see Shale Daily, Oct. 25). At the same time, increasing volumes of fracking waste, mostly trucked in from out of state, and a desire from operators to recycle more of that waste for reuse found state legislators approving the use of wastewater storage impoundments over the summer, leading ODNR to craft new rules for the temporary pits and recycling facilities (see Shale Daily, Oct. 11).Ohio’s pipeline standards were last updated in 2009. The standards provide guidelines and recommendations to help rural landowners and farmers restore soil productivity and agricultural drainage after the installation of pipelines.The standards are not a mandatory requirement, but instead they offer a technical resource that midstream companies, landowners and farmers can use to minimize the impacts of pipeline construction on Ohio’s soil and water resources. The updates to the state’s standards were announced on Friday. In October, ODNR also said it was working on new rules that would govern large football field-sized wastewater impoundments. The pits have been employed by operators in other parts of the Appalachian Basin, primarily as a source of water in dry areas, or as a tool to reduce truck traffic and reuse the water in a closed-loop system.ODNR had said it hoped to complete those rules by the end of the year, but only draft regulations have been completed to date. Before the rule change, Ohio regulations permitted the use of lined impoundments for the temporary storage of freshwater for drilling, but allowed wastewater to only be stored in above ground covered steel tanks. Starting in January, Ohio will begin permitting the wastewater impoundments.The proposed rules call for plastic liners and monitors that could detect leaks and help protect groundwater and storage tanks would get ledges to contain spills.More wastewater recycling plants are planned for the state as well, and early proposals would call for their placement far away from streams and parts of the state prone to flooding.Last year, Ohio injected 14.2 million barrels of waste in underground wells.
Summit Midstream to Enter Utica Shale, Buy Assets for $190M
Summit Midstream Partners LLC, which operates in shale plays across the country, plans to enter the Utica Shale after agreeing to acquire Blackhawk Midstream LLC’s interest in two companies operating and developing midstream infrastructure in southeastern Ohio for $190 million.
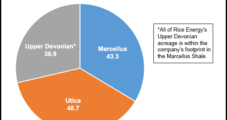
Rice Energy Unveils Operations in $800M IPO
Rice Energy Inc. unveiled sound prospects in documents filed for an $800 million public offering, shining a light on the small independent’s prime acreage in the Appalachian Basin where it plans to step on the gas in the years ahead, starting with a $1.08 billion capital budget next year.
Focused on Efficiency, Halcon Lowers 2014 Budget
Halcon Resources Corp. said Monday it was lowering its 2014 capital expenditures budget by 14%, bringing it from a previously announced $1.1 billion to approximately $950 million — most of which will be spent in the Bakken and Eagle Ford Shale plays.
EVEP CEO Deems Utica a Key Growth Driver
Even with about 60% of the company’s production and capital spending still tied up in the Barnett Shale, EV Energy Partners LP (EVEP) CEO Mark Houser wasn’t shy about calling Ohio’s Utica Shale play the “key driver of the EVEP story” last week at the Wells Fargo Energy Symposium in New York.
Kinder, NOVA Chemicals Plan Utica-Michigan Products Pipeline
Kinder Morgan Energy Partners LP’s Kinder Morgan Cochin LLC unit has agreed with NOVA Chemicals Corp. to develop a 210-mile, 10-inch diameter products pipeline from the Utica Shale to Michigan, where it would feed Kinder’s Cochin Pipeline.




